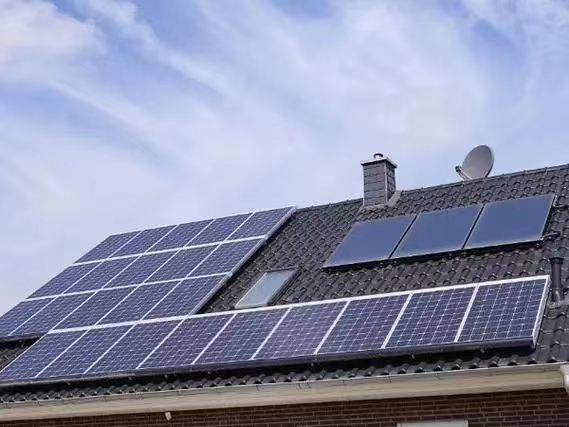
Solar roof technology has emerged as a pivotal element in global efforts to transition towards sustainable energy solutions. It involves the installation of solar power generation devices on the roofs of buildings, utilizing solar photovoltaic technology to generate power. This approach aligns with urban and rural construction goals, aiming to achieve energy conservation and emission reduction. Various countries have initiated solar roof plans driven by policy incentives, reflecting a global consensus on the need for renewable and clean energy sources.
Two predominant technical routes are employed for installing solar power generation systems on roofs: Building Applied Photovoltaics (BAPV) and Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV). BAPV represents the traditional method of installing photovoltaic modules on existing buildings' surfaces for power generation. On the other hand, BIPV is a more advanced technology that integrates solar power generation products directly into the building structure. In this approach, photovoltaic elements become an integral part of the building, serving both structural and power generation functions.
The international market has long recognized the potential of solar panels. As one of the most promising renewable and clean energy sources in the 21st century, solar energy has captured the attention of global stakeholders. The European Union (EU), in particular, views solar energy as a highly competitive power source. Combining solar energy capacity with enhanced energy conversion efficiency can protect European citizens from the impact of oil fuel price fluctuations. To harness this potential, the EU has introduced the European Solar Roof Plan as part of its broader solar energy strategy.
The EU aims to meet nearly 25% of power consumption through building photovoltaic installations on rooftops, surpassing the current share of natural gas. This ambitious plan seeks to unlock the solar power generation potential of underutilized rooftops, contributing to a cleaner, safer, and more affordable energy landscape in Europe. To expedite this goal, the EU took immediate action before the end of 2022.
In Japan, a similar commitment to solar power is evident through regulations mandating the installation of solar panels on new residential buildings in the Tokyo Metropolitan area starting from April 2025. This initiative is a significant step towards reducing household carbon emissions and leveraging building rooftops for solar power projects. The impact is substantial, with an estimated increase in solar power generation capacity of 40,000 kilowatts per year.
China, despite having almost no solar power generation equipment on rooftops until 2016, has rapidly adopted solar power technologies. The country now installs solar power generation equipment equivalent to the capacity of 12 to 25 nuclear power plants annually. Government subsidies, covering 30% to 50% of production costs for relevant enterprises, have been instrumental in this growth. However, the mixed quality of China's photovoltaic enterprises presents challenges in achieving a systematic and healthy improvement in technical standards through initiatives like the "roof plan."
As of now, China is actively promoting the integration demonstration of photovoltaic buildings, including solar roofs and photovoltaic curtain walls, in large and medium-sized cities with developed economies. The year 2020 marked China's entry into the era of a moderately prosperous society, coupled with a focus on poverty alleviation and rural revitalization. Promoting rural household photovoltaic installations to establish a stable income aligns with these objectives. The active support for off-grid power generation in rural and remote areas, along with regulations facilitating power transmission to the countryside, underscores the role of solar energy technology in achieving these goals.
Focusing on the integration of solar roofs, photovoltaic curtain walls, and other photovoltaic buildings can showcase the immediate benefits of solar energy application. This approach not only provides short-term advantages but also stimulates enthusiasm for large-scale promotion and encourages industrial capital investment in solar energy.
Despite the positive momentum, challenges persist. While many households and office buildings respond actively to solar roof plans, the overall coverage remains relatively low due to the significant investment required for solar panel installation. Concerns about installation costs and potential roof damage during the installation process contribute to hesitancy among potential adopters. Moreover, the weather-dependent nature of solar panels affects their efficiency in regions with insufficient sunlight, impacting power consumption during overcast or less sunny periods.Feel free to reach out to us, our experts are here to assist you every step of the way.
In conclusion, while solar roof plans hold immense promise, addressing challenges related to installation costs, quality standards, and weather dependence is crucial for their widespread adoption. The incorporation of innovative technologies, such as Tesla solar tiles, can significantly enhance the overall efficiency and appeal of solar power systems. As the world collectively strives for sustainable energy solutions, continual advancements and strategic initiatives are essential to unlock the full potential of solar energy in diverse global contexts.
If you're interested in learning more about our solar energy storage offerings, we encourage you to explore our product line. We offer a range of panels and battery that are designed for various applications and budgets, so you're sure to find the right solution for your needs.
Website:www.fgreenpv.com
Email:Info@fgreenpv.com
WhatsApp:+86 17311228539
Post time: Dec-24-2023