With the increasing frequency of natural disasters worldwide, many homeowners are considering solar photovoltaic (PV) systems as a solution to avoid power outages. But does installing a solar PV system guarantee a constant power supply during these disruptions? The answer depends on the type of solar PV system you have installed. Today, we will discuss the different types of solar PV systems and their practical applications in daily life.
Based on current market offerings and various application scenarios, solar PV systems can be broadly categorized into four types: grid-tied systems, off-grid systems, hybrid systems, and microgrid systems.
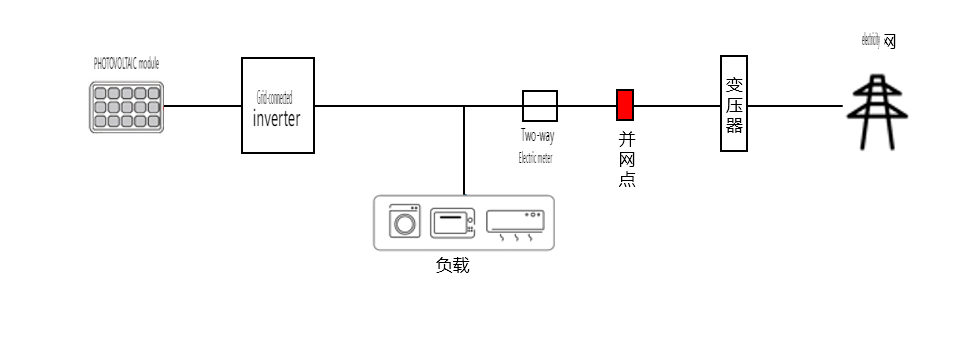
**1. Grid-Tied PV System**
A grid-tied PV system comprises PV modules, a grid-tied inverter, loads, a bidirectional meter, a grid-tied cabinet, and the utility grid.
**How It Works:** The PV modules generate direct current (DC) electricity, which the inverter converts to alternating current (AC) electricity. This electricity powers the household, and any excess is fed into the grid.
**Features:**
1. **Grid Connection:** Supplies electricity to the grid, either partially or entirely.
2. **Outage Dependency:** Stops generating electricity during a grid outage due to anti-islanding features for safety.
3. **Nighttime Dependency:** Relies on grid electricity at night.
4. **No Storage:** Lacks energy storage capabilities.
Grid-tied systems are commonly used in urban and suburban areas with reliable grid infrastructure. However, they are not immune to power outages, as safety regulations require these systems to shut down during grid failures to prevent electrical backfeed that could endanger repair crews.
---
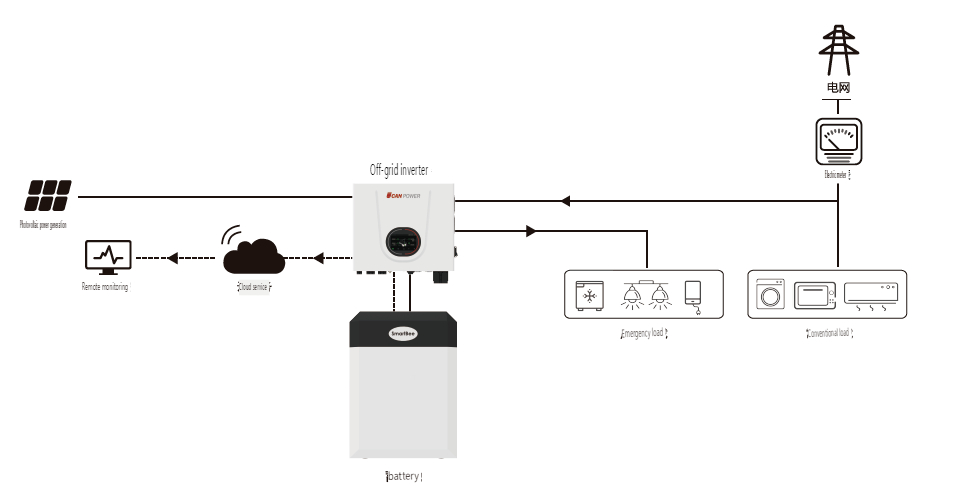
**2. Off-Grid PV System**
Off-grid PV systems operate independently of the grid and comprise PV modules, an off-grid inverter, batteries, and loads. Advanced solutions, such as UON's UFox series, integrate the inverter and battery into a single unit. These systems are ideal for remote areas, un-electrified regions, islands, communication base stations, and street lighting.
**How It Works:** Sunlight is converted into electricity to power loads and charge batteries via the off-grid inverter. The system can also charge batteries from the grid if necessary. During periods without sunlight or grid outages, the stored battery power supplies the loads.
**Features:**
1. **Independence:** Operates independently of the grid, providing power as long as there is sufficient sunlight.
2. **Storage Requirement:** Requires batteries for nighttime and cloudy weather operation.
3. **Flexibility:** Can function without PV modules, using batteries alone.
Off-grid systems are crucial for locations without grid access, ensuring that these areas have a reliable power source. The main limitation is the need for substantial battery storage to cover periods of low solar input.
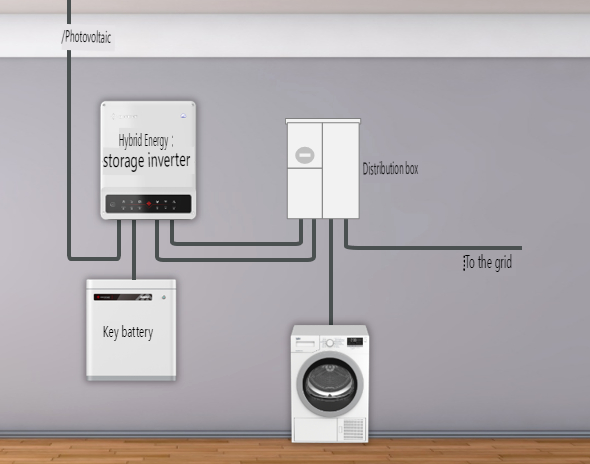
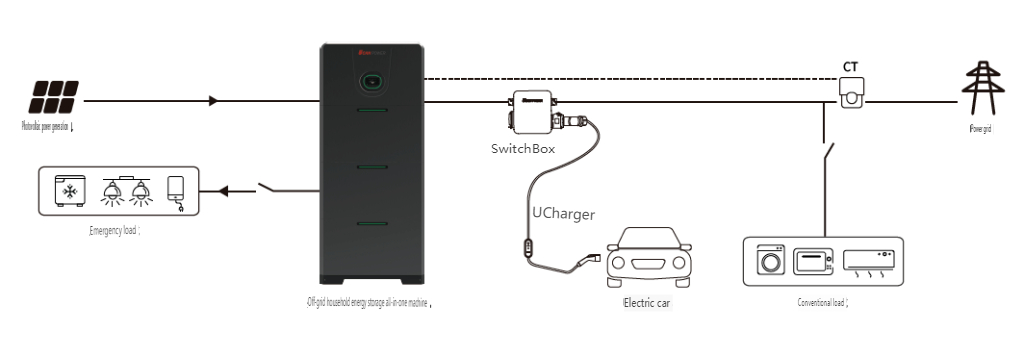
**3. Hybrid PV System**
Hybrid systems integrate grid-tied and off-grid features, including PV modules, a hybrid inverter, batteries, and loads. Advanced solutions, like UON's UHome series, combine the hybrid inverter and battery into one unit. Hybrid systems are suitable for areas with frequent outages or where self-consumption of solar power is preferred over feeding excess power to the grid.
**How It Works:** During daylight, the hybrid inverter prioritizes supplying power to the loads and storing excess power in the batteries. At night, the batteries supply power to the loads via the hybrid inverter. The system can switch to off-grid mode during grid outages, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
**Features:**
1. **Versatility:** Combines the benefits of grid-tied and off-grid systems, allowing for grid power sales and continuous operation during outages.
2. **Storage Necessity:** Requires batteries to function without the grid.
3. **Flexibility:** Can operate without PV modules, utilizing batteries for peak load shifting or emergency backup.
Hybrid systems offer the best of both worlds, providing reliability and flexibility. They are especially useful in areas with unstable grids or where energy independence is a priority.
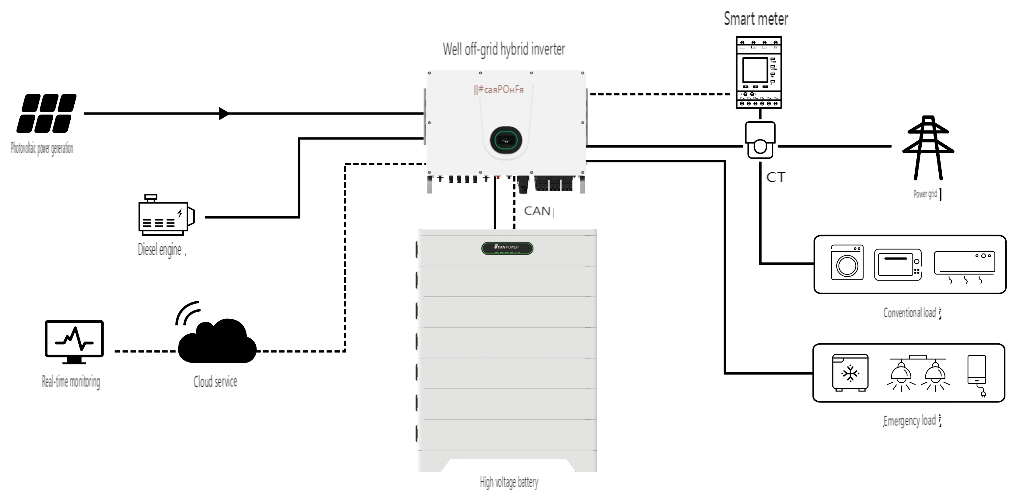
**4. Microgrid System**
A microgrid system consists of distributed energy sources (PV, wind, diesel), loads, an energy storage system, and control devices, forming a local power distribution network. It converts and supplies locally generated energy to nearby loads.
**Features:**
Microgrid systems can operate autonomously, managing and protecting themselves, or connect to external grids. They address distributed energy integration issues, promoting large-scale adoption of renewable energy and supporting smart grid implementation.
Microgrids are beneficial for communities or businesses looking to improve energy resilience and sustainability. They can function independently from the main grid, making them a robust solution for critical infrastructure.
---
**Conclusion**
These four types of solar PV systems cater to different needs, offering versatile solutions for households and businesses seeking green energy. UON, a technology-driven company focused on power storage solutions, offers a range of products and solutions, including home grid-tied storage systems, off-grid storage systems, decentralized commercial storage, and portable storage systems to meet your energy needs across all scenarios.
If you're interested in learning more about our solar energy storage offerings, we encourage you to explore our product line. We offer a range of panels and battery that are designed for various applications and budgets, so you're sure to find the right solution for your needs.
Website:www.fgreenpv.com
Email:Info@fgreenpv.com
WhatsApp:+86 17311228539
Post time: May-25-2024