As the world increasingly embraces renewable energy, integrated solar, storage, and charging solutions (often referred to as "solar-storage-charging") have become essential in ensuring that solar power is effectively harnessed, stored, and utilized. In this blog, we'll explore the principles behind these solutions, the components involved, and their typical applications, using a case study of a GREEN POWER integrated solar, storage, and charging system.
Typical Applications
One of the most common applications for an integrated solar-storage-charging system is in community-scale solar projects. For instance, in county-wide solar initiatives, it is common to construct solar carports in communal areas like streets or village squares. These carports are equipped with solar panels, storage batteries, and charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs).
Imagine a solar carport with 20 standard parking spaces, covering an area of approximately 320 square meters. The carport itself is expanded to 500 square meters to accommodate solar panels. By installing around 200 units of 550W panels (each occupying about 2.5 square meters), the total solar power generation capacity can reach 110 kW.
When designing such a system, storage battery configuration is crucial. Given space constraints, a distributed storage cabinet design is often preferred to minimize the footprint. For example, a 100kW/209kWh storage system could be implemented, discharging at 0.5C, which could provide 100 kW of power for about 1.8 hours at full load. Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are typically used for this purpose due to their high power density and safety features.
The charging stations can be configured in a split-body design, allowing flexibility based on the specific power output of the transformers and storage systems. Both AC and DC charging stations are compatible, depending on the project's needs.
Principles and Components of the Solar-Storage-Charging System
An integrated solar-storage-charging system typically consists of several key components:
1. **Solar Panels**: Made from crystalline silicon, these panels convert solar energy into electricity. They are designed to withstand various weather conditions, including rain, hail, and wind. The panels can be connected in series and parallel configurations to meet the desired power output.
2. **Grid-tied Inverter**: This device converts the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that meets the grid's requirements.
3. **Energy Storage System (ESS)**: This includes the storage batteries, which store excess electricity generated by the solar panels. In our example, a 209kWh LiFePO4 battery system is used, known for its safety and efficiency.
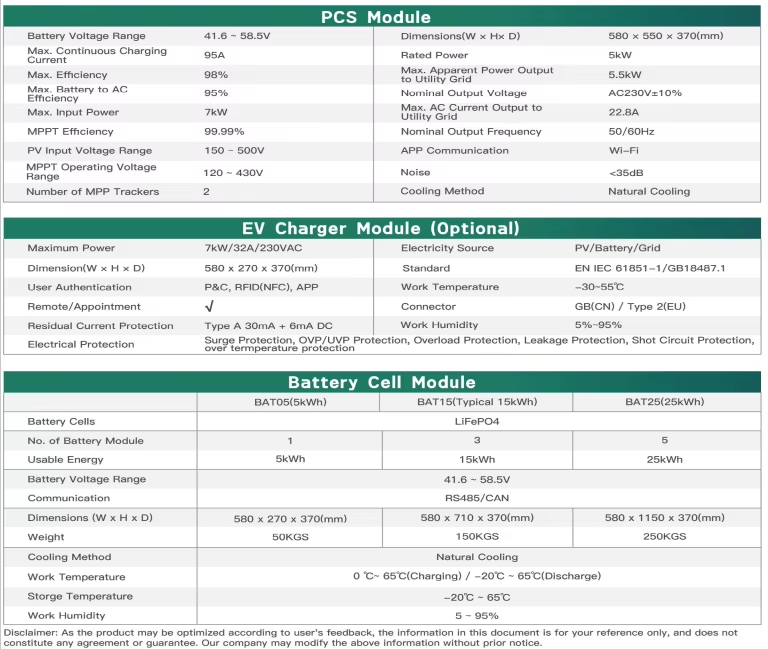
4. **Power Conversion System (PCS)**: The PCS controls the charging and discharging of the storage batteries, managing the conversion between DC and AC. It communicates with the Battery Management System (BMS) to ensure the batteries are charged and discharged safely.
5. **AC Distribution Cabinet**: This cabinet connects the inverter and PCS to the grid, incorporating various protective devices such as circuit breakers, surge protectors, and metering systems.
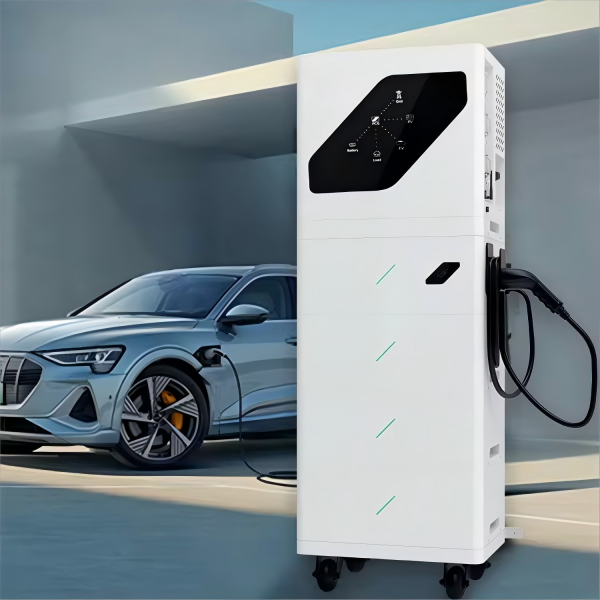
6. **Charging Stations**: These stations act as the load for the system, providing power to electric vehicles. They can be tailored to the project's specific needs, with options for both AC and DC charging.
7. **Monitoring System**: A comprehensive monitoring system collects data from the solar panels, ESS, and charging stations, uploading it to a cloud-based management platform. This allows for real-time monitoring and control of the entire system.
System Design and Integration
The overall design of an integrated solar-storage-charging system involves several critical steps:
1. **Solar Power System Design**: In our example, the solar panels are configured to produce 110kWp, with the option to adjust based on the available carport area. The inverter is sized accordingly, either with a single 110kW unit or two 50kW units.
2. **Energy Storage System Design**: The storage system uses a distributed "All in One" design, which is more flexible and offers a variety of capacity options. For example, the ENSE 209KWH-2H1 smart storage cabinet integrates a 209kWh battery and a 100kW PCS in a single enclosure.
3. **Charging Station Configuration**: Charging stations are considered electrical loads within the system. Their configuration depends on the available capacity of the transformer. If the storage system is entirely responsible for powering the charging stations, the PCS must be sized accordingly. A scalable solution might involve multiple 100kW PCS units working in parallel.
4. **Control and Monitoring Systems**: The system is managed through a centralized controller that integrates the BMS, fire safety, HVAC, monitoring, and energy management systems (EMS). The monitoring system ensures that all components, including the solar panels, storage units, and charging stations, operate optimally.
System Operation Logic
The operation of an integrated solar-storage-charging system is governed by the relationship between solar power generation and the charging station load:
- **When Solar Output ≤ Charging Load**: All solar-generated power is used to charge the vehicles, with any shortfall supplemented by the grid.
- **When Solar Output > Charging Load**: The excess power is stored in the batteries, which can be discharged during peak electricity pricing periods to optimize costs.
Detailed Component Breakdown
Let's dive deeper into the components used in the system:
Solar Panels
In this project, the solar panels are conventional monocrystalline modules, each with an area of 2.5 square meters and a power rating of 550W. A total of 200 panels are installed over an area of 520 square meters, providing a combined power output of 110kW. With an average daily generation of 3.2 hours of full power, the system is expected to generate approximately 120,000 kWh annually.
Grid-Tied Inverter
The inverter is a crucial element in the solar power system, converting DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity. The selected model is a 110kW inverter, designed to meet the specific needs of this project.
Energy Storage System
The ESS is a key component, ensuring that excess solar power is stored for later use. The ENSE 209KWH-2H1 smart storage cabinet integrates a 209kWh LiFePO4 battery and a 100kW PCS, enabling efficient power management.
Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS monitors the battery's voltage, current, and temperature, ensuring safe and efficient operation. It also manages the charging and discharging processes, prolonging the battery's lifespan and maintaining system stability.
Charging Stations
For this project, the charging stations include a combination of 7kW AC units and 60kW DC units, providing flexibility in charging options. The stations are equipped with various interfaces for user interaction, including card swiping and mobile payments.
Monitoring System
GREEN POWER's Smart Energy Manager (SEM) serves as the localized energy management hub, allowing for real-time data monitoring and integration with higher-level EMS units. The system supports remote monitoring and control, providing valuable insights into the system's performance.
Conclusion
GREEN POWER's integrated solar-storage-charging solutions offer a comprehensive approach to renewable energy management. By combining solar power generation, energy storage, and EV charging into a single, cohesive system, these solutions provide a flexible and scalable way to meet the growing demand for clean energy. Whether it's for a community project or a larger-scale installation, GREEN POWER's systems are designed to optimize energy use, reduce costs, and promote sustainability.
If you're interested in learning more about our solar energy storage offerings, we encourage you to explore our product line. We offer a range of panels and battery that are designed for various applications and budgets, so you're sure to find the right solution for your needs.
Website:www.fgreenpv.com
Email:Info@fgreenpv.com
WhatsApp:+86 17311228539
Post time: Sep-01-2024